Contents
- Some examples of digital filters for images
- notation
- Linear Filters
- shift filter
- Gaussian Filters
- The impulse response of a filter can be computed as the convolution against a Dirac
- Generating a noisy image as an image corrupted by additive Gaussian white noise
- denoising via smoothing (see slides and possibly LASIP package)
Some examples of digital filters for images
Giacomo Boracchi
close all
clear
clc
notation
% I original image % h LTI discrete filter % G convolution output % n noise % z noisy observation
Linear Filters
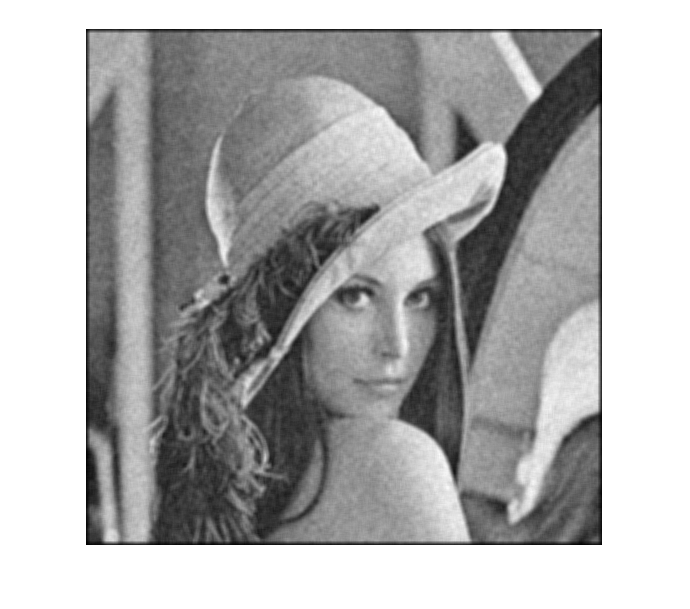
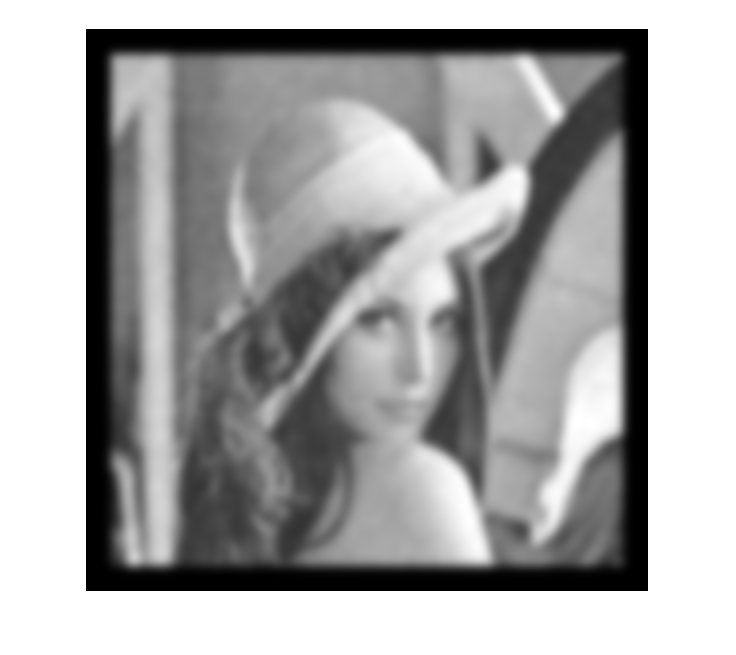
FILTER_SIZE = 21; % load image check the filename!! I = im2double(imread('image_lena512.png')); figure(1), imshow(I, []), title('I, original image') % have a look at the image size whos I % create averaging filter h = ones(FILTER_SIZE)/(FILTER_SIZE^2); % generate "averaged" image G = conv2(I, h); % have a look at size of convolution whos G G = conv2(I, h, 'same'); % use the option same to keep image size constant whos G % display the original image and the distribution of pixel intensities figure(1), imshow(I,[]),title('input original') figure(2), imshow(G,[]),title('convolved output') % generate "averaged" image z2 = conv2(h, I, 'same'); % display the original image and the distribution of pixel intensities figure(1), imshow(I,[]),title('input original') figure(2), imshow(G,[]),title('convolved output')
Name Size Bytes Class Attributes I 512x512 2097152 double Name Size Bytes Class Attributes G 532x532 2264192 double Name Size Bytes Class Attributes G 512x512 2097152 double


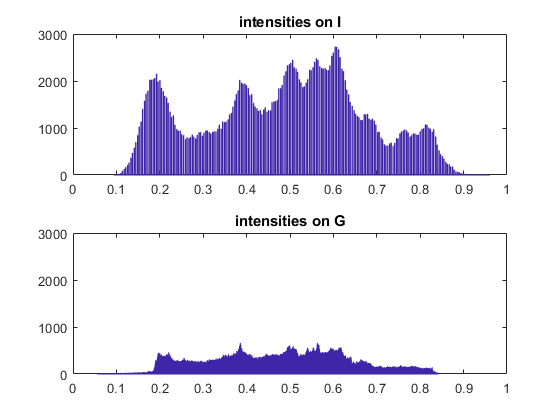
While intensities of I are values like {i/255, i = 0,.., 255} there are much more values in G thanks to the local smoothing
figure(4), subplot(2,1,1), hist(I(:) , 1000), title('intensities on I'), axis([0 1 0 3000]) subplot(2,1,2), hist(G(:) , 1000), title('intensities on G'), axis([0 1 0 3000])
shift filter
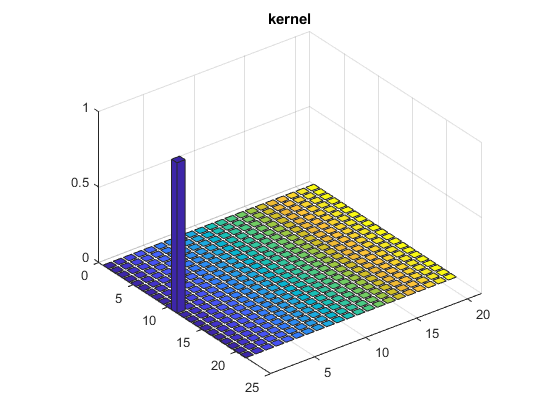
FILTER_SIZE = 21; h=zeros(FILTER_SIZE ); h((FILTER_SIZE - 1) / 2 + 1 ,1) = 1; G=conv2(I, h, 'same'); % display figure(1), imshow(I),title('original') figure(2), imshow(G),title('observation') figure(3), bar3(h),title('kernel')


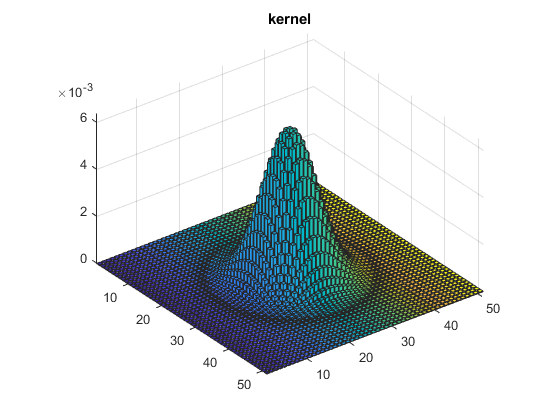
Gaussian Filters
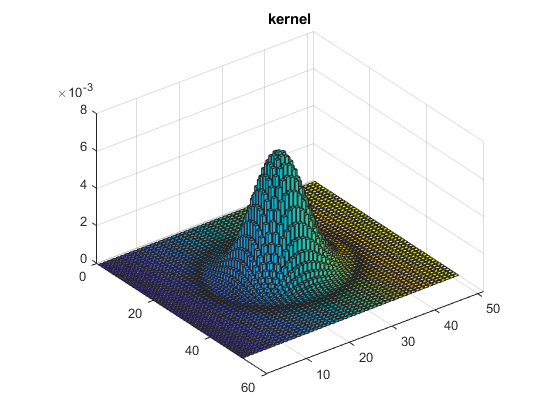
h_size = 51; sigma_gauss = 5; h = fspecial('gaussian' , h_size , sigma_gauss); figure(3),bar3(h),title('kernel') G=conv2(I , h , 'same'); % display figure(1), imshow(I),title('original') figure(2), imshow(G),title('observation') figure(3), bar3(h),title('kernel')


The impulse response of a filter can be computed as the convolution against a Dirac
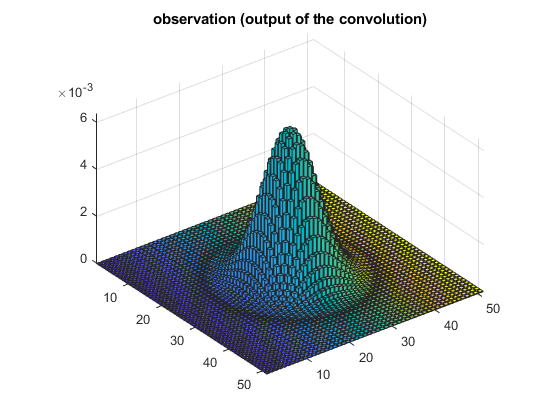
close all I = zeros(51); I(26 , 26) = 1; G=conv2(I , h , 'same'); % display figure(1), imshow(I),title('original image (Dirac)') figure(2), imshow(G, []), title('observation (output of the convolution)') figure(3), bar3(G),title('observation (output of the convolution)'), axis tight % check that it corresponds to the kernel figure(4), bar3(h),title('kernel'), axis tight


Generating a noisy image as an image corrupted by additive Gaussian white noise
I=im2double(imread('image_lena512.png')); figure(1), imshow(I,[]),title('I, original image') sigma_noise = 0.1; % the noise is a matrix having the same sizes of the original image n = sigma_noise * randn(size(I)); figure(4), imshow(n, []) % Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN): the noisy observation is given by z = I + n; figure(5),imshow(G);


denoising via smoothing (see slides and possibly LASIP package)
% suppress noise by averaging: each pixel is replaced by the average over a 7x7 neighboor, uniform weight figure(6),imshow(conv2(z, ones(5)/(5^2)),[]) % suppress noise by averaging: each pixel is replaced by the average over a neighbor defined by the Gaussian kernel, % which also defines the averaging weights figure(7),imshow(conv2(z, h),[])

